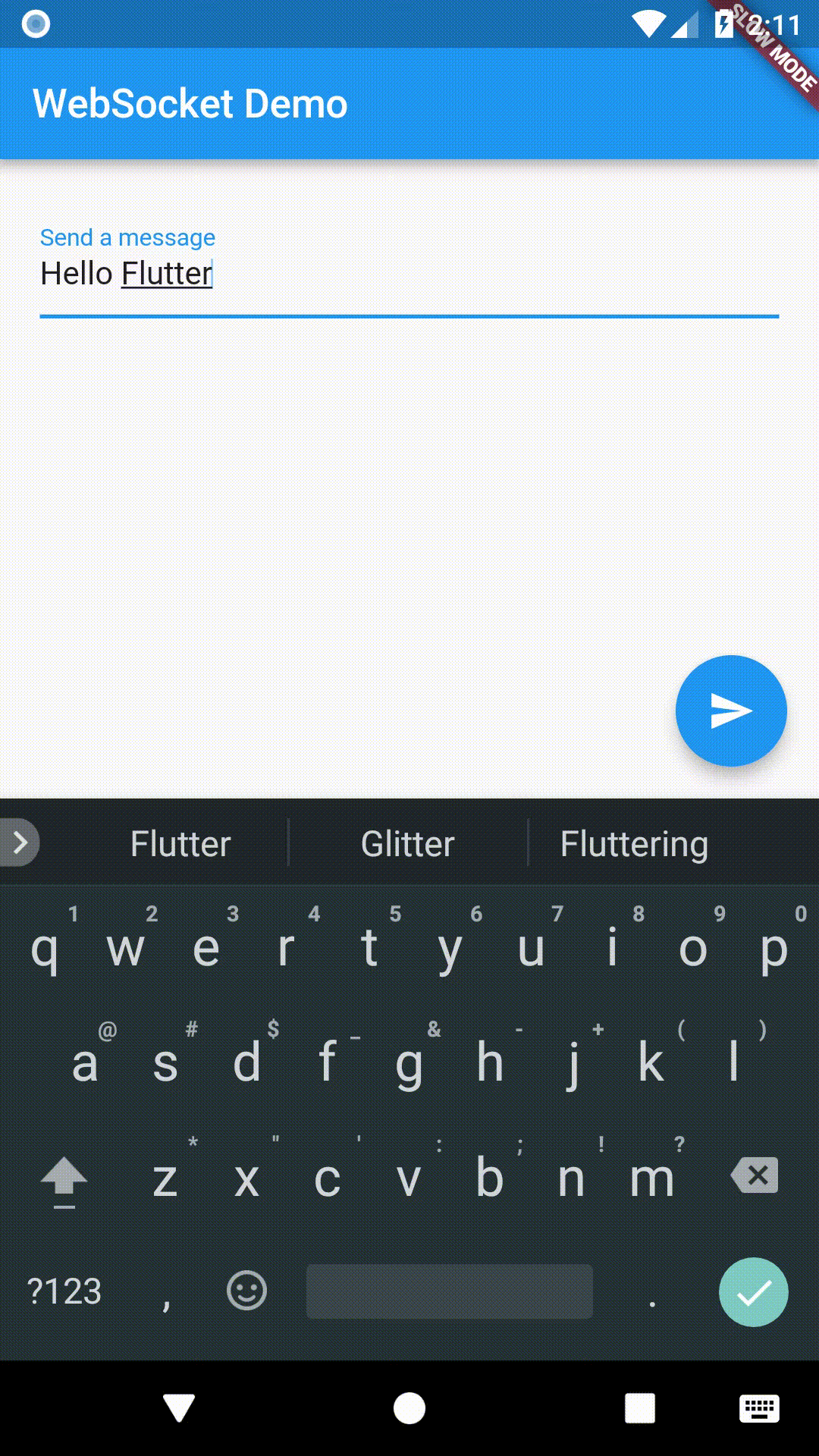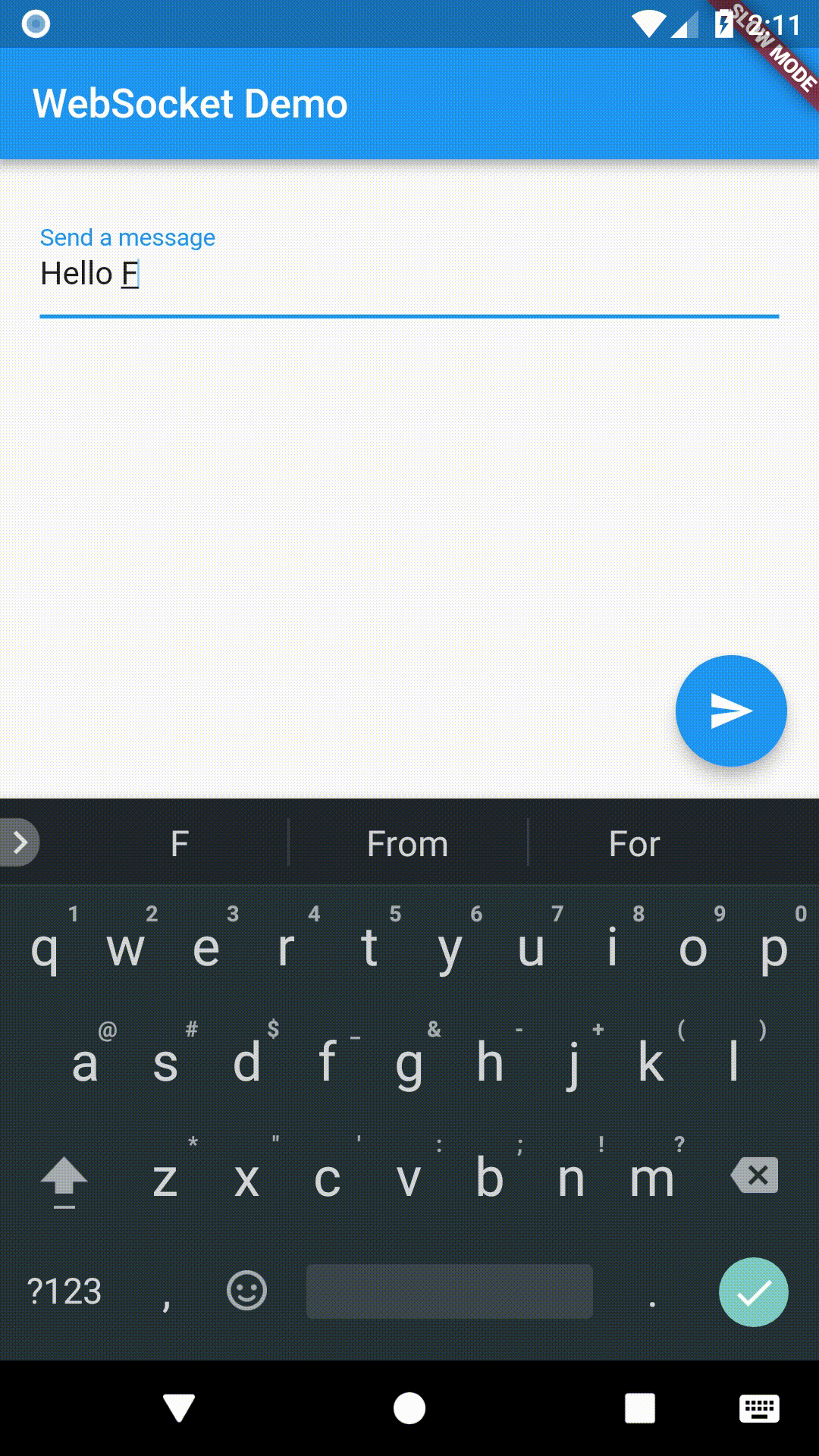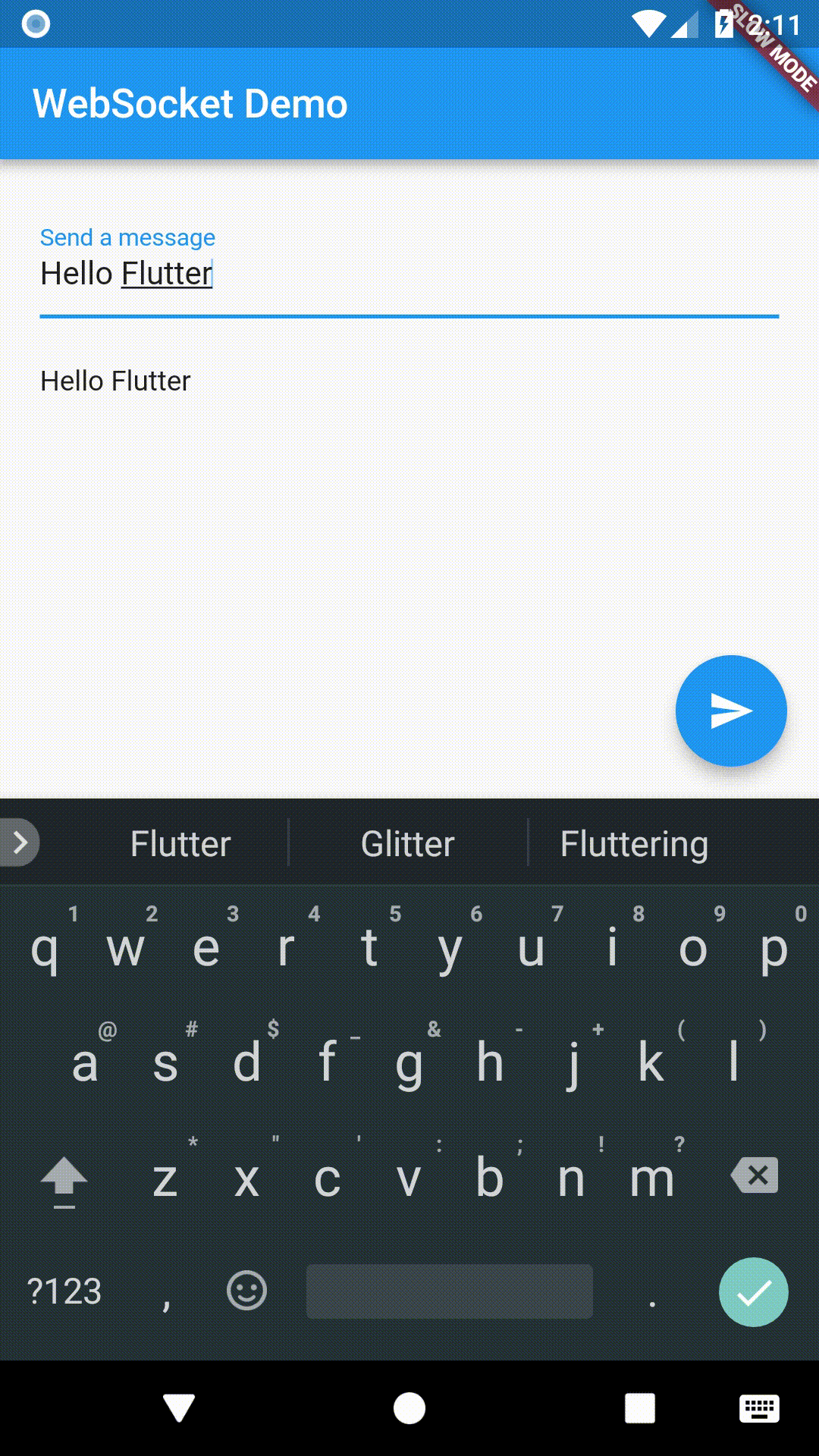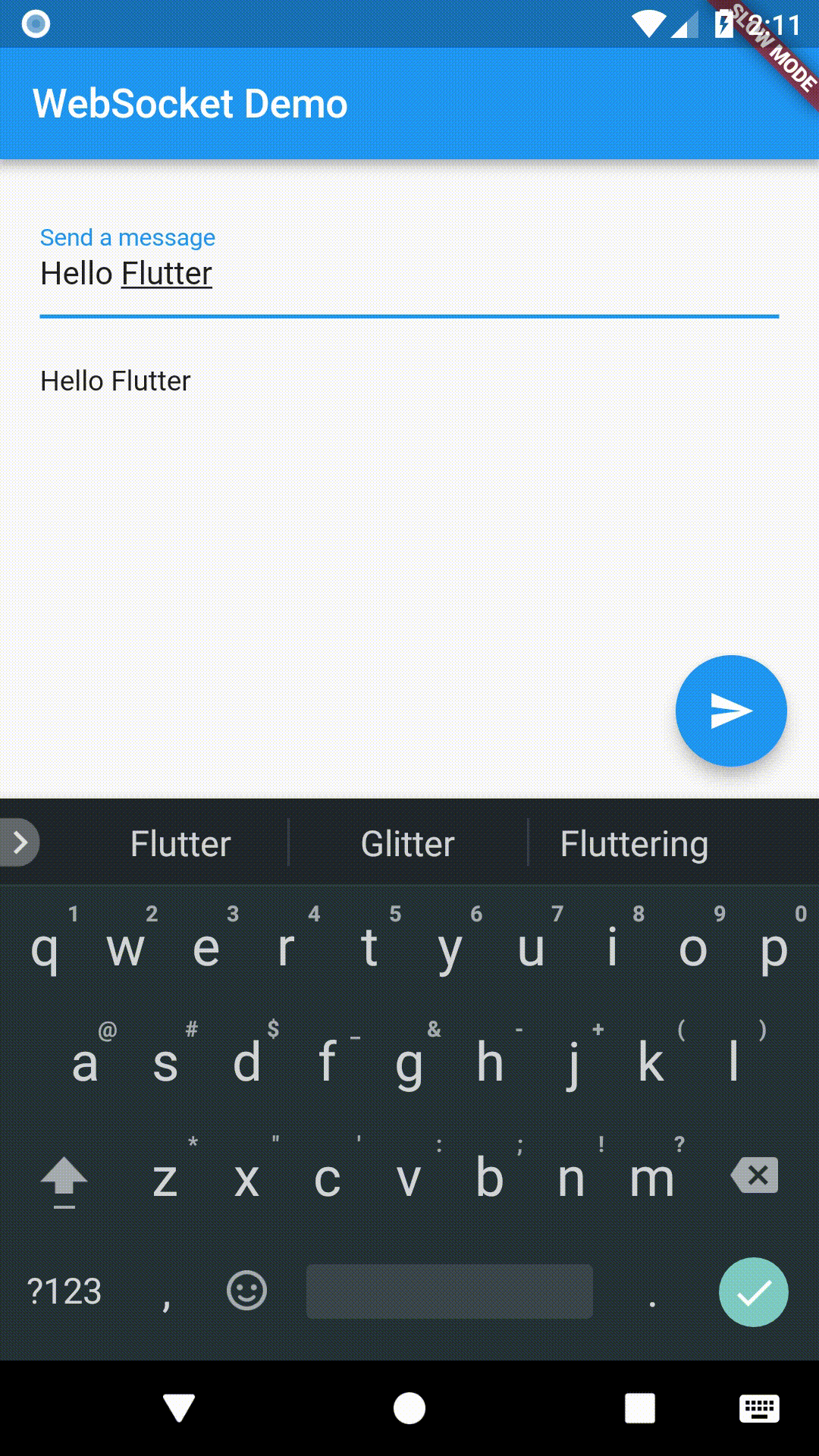
Working with WebSockets
In addition to normal HTTP requests, we can connect to servers using WebSockets. WebSockets allow for two-way communication with a server without polling.
In this example, we’ll connect to a test server provided by websocket.org. The server will simply send back the same message we send to it!
Directions
- Connect to a WebSocket server
- Listen for messages from the server
- Send Data to the Server
- Close the WebSocket connection
1. Connect to a WebSocket server
The web_socket_channel package provides the tools we’ll need to connect to a WebSocket server.
The package provides a WebSocketChannel that allows us to both listen for
messages from the server as well as push messages to the server.
In Flutter, we can create a WebSocketChannel that connects to a server in one
line:
final channel = new IOWebSocketChannel.connect('ws://echo.websocket.org');
2. Listen for messages from the server
Now that we’ve established a connection, we can listen to messages from our server.
After we send a message to the test server, it will send the same message back.
How do we listen for messages and display them? In this example, we’ll use
a StreamBuilder
Widget to listen for new messages and a Text
Widget to display them.
new StreamBuilder(
stream: widget.channel.stream,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
return new Text(snapshot.hasData ? '${snapshot.data}' : '');
},
);
How does this work?
The WebSocketChannel provides a Stream
of messages from the server.
The Stream class is a fundamental part of the dart:async package. It
provides a way to listen to async events from a data source. Unlike Future,
which returns a single async response, the Stream class can deliver many
events over time.
The StreamBuilder
Widget will connect to a Stream and ask Flutter to rebuild every time it
receives an event using the given builder function!
3. Send Data to the Server
In order to send data to the server, we’ll add messages to the sink provided
by the WebSocketChannel.
channel.sink.add('Hello!');
How does this work
The WebSocketChannel provides a StreamSink
to push messages to the server.
The StreamSink class provides a general way to add sync or async events to a
data source.
4. Close the WebSocket connection
After we’re done using the WebSocket, we’ll want to close the connection! To do
so, we can close the sink.
channel.sink.close();
Complete Example
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'package:web_socket_channel/io.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:web_socket_channel/web_socket_channel.dart';
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final title = 'WebSocket Demo';
return new MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: new MyHomePage(
title: title,
channel: new IOWebSocketChannel.connect('ws://echo.websocket.org'),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
final WebSocketChannel channel;
MyHomePage({Key key, @required this.title, @required this.channel})
: super(key: key);
@override
_MyHomePageState createState() => new _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
TextEditingController _controller = new TextEditingController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text(widget.title),
),
body: new Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: new Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
new Form(
child: new TextFormField(
controller: _controller,
decoration: new InputDecoration(labelText: 'Send a message'),
),
),
new StreamBuilder(
stream: widget.channel.stream,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
return new Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 24.0),
child: new Text(snapshot.hasData ? '${snapshot.data}' : ''),
);
},
)
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: new FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _sendMessage,
tooltip: 'Send message',
child: new Icon(Icons.send),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
void _sendMessage() {
if (_controller.text.isNotEmpty) {
widget.channel.sink.add(_controller.text);
}
}
@override
void dispose() {
widget.channel.sink.close();
super.dispose();
}
}