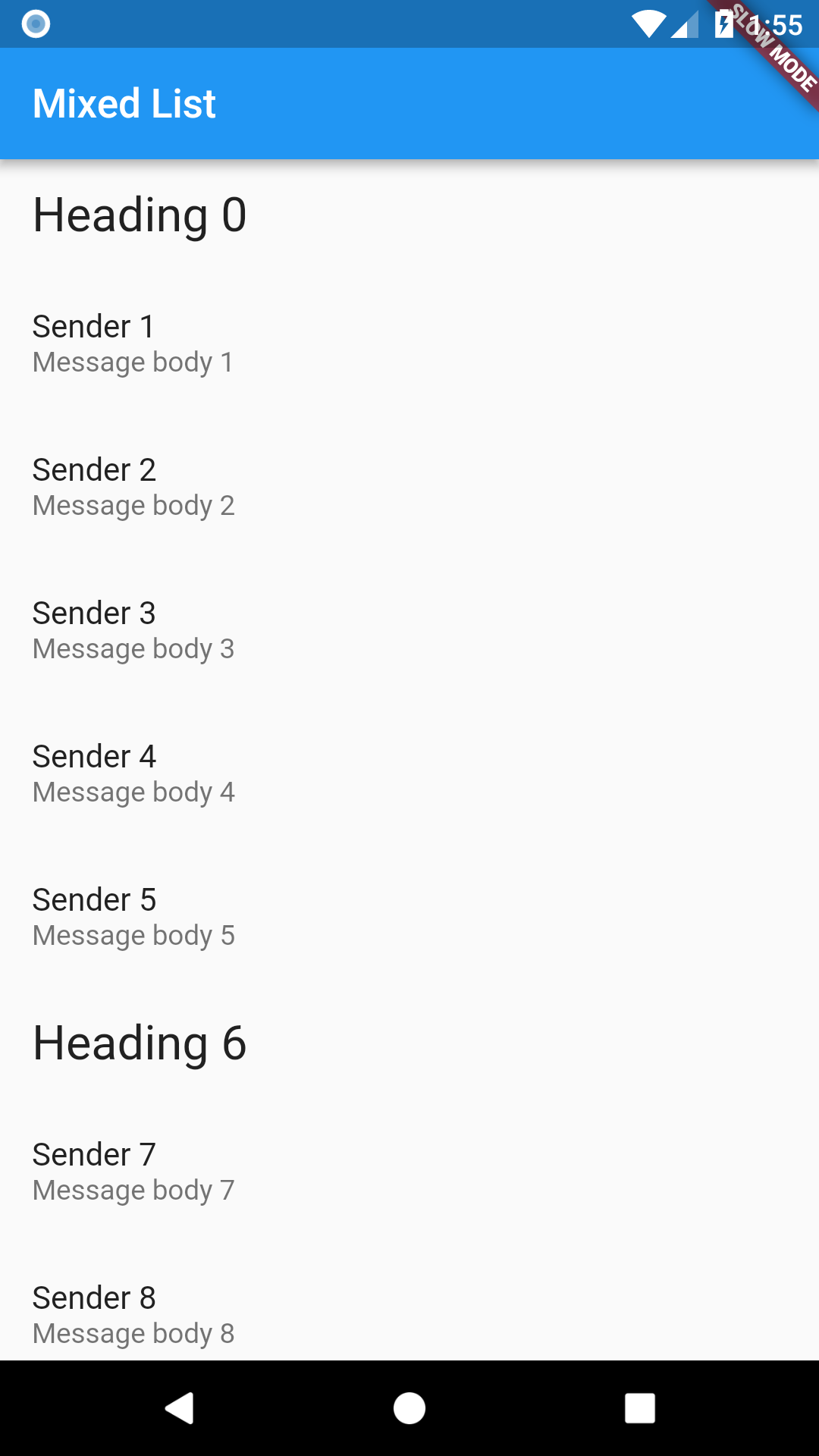
Creating lists with different types of items
We often need to create lists that display different types of content. For example, we might be working on a List that shows a heading followed by a few items related to the heading, followed by another heading, and so on.
How would we create such a structure with Flutter?
Directions
- Create a data source with different types of items
- Convert the data source into a List of Widgets
1. Create a data source with different types of item
Types of Items
In order to represent different types of items in a List, we’ll need to define a class for each type of item.
In this example, we’ll work on an app that shows a header followed by five
messages. Therefore, we’ll create three classes: ListItem, HeadingItem,
and MessageItem.
// The base class for the different types of items the List can contain
abstract class ListItem {}
// A ListItem that contains data to display a heading
class HeadingItem implements ListItem {
final String heading;
HeadingItem(this.heading);
}
// A ListItem that contains data to display a message
class MessageItem implements ListItem {
final String sender;
final String body;
MessageItem(this.sender, this.body);
}
Create a List of Items
Most of the time, we’d fetch data from the internet or a local database and convert that data into a list of items.
For this example, we’ll generate a list of items to work with. The list will contain a header followed by five messages. Rinse, repeat.
final items = new List<ListItem>.generate(
1200,
(i) => i % 6 == 0
? new HeadingItem("Heading $i")
: new MessageItem("Sender $i", "Message body $i"),
);
2. Convert the data source into a List of Widgets
In order to handle converting each item into a Widget, we’ll employ the
ListView.builder
constructor.
In general, we’ll want to provide a builder function that checks for what type
of item we’re dealing with, and returns the appropriate Widget for that type of
item.
In this example, using the is keyword to check the type of item we’re dealing
with can be handy. It’s fast, and will automatically cast each item to the
appropriate type. However, there are different ways to approach this problem if
you prefer another pattern!
new ListView.builder(
// Let the ListView know how many items it needs to build
itemCount: items.length,
// Provide a builder function. This is where the magic happens! We'll
// convert each item into a Widget based on the type of item it is.
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final item = items[index];
if (item is HeadingItem) {
return new ListTile(
title: new Text(
item.heading,
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headline,
),
);
} else if (item is MessageItem) {
return new ListTile(
title: new Text(item.sender),
subtitle: new Text(item.body),
);
}
},
);
Complete Example
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(new MyApp(
items: new List<ListItem>.generate(
1000,
(i) => i % 6 == 0
? new HeadingItem("Heading $i")
: new MessageItem("Sender $i", "Message body $i"),
),
));
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
final List<ListItem> items;
MyApp({Key key, @required this.items}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final title = 'Mixed List';
return new MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text(title),
),
body: new ListView.builder(
// Let the ListView know how many items it needs to build
itemCount: items.length,
// Provide a builder function. This is where the magic happens! We'll
// convert each item into a Widget based on the type of item it is.
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final item = items[index];
if (item is HeadingItem) {
return new ListTile(
title: new Text(
item.heading,
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headline,
),
);
} else if (item is MessageItem) {
return new ListTile(
title: new Text(item.sender),
subtitle: new Text(item.body),
);
}
},
),
),
);
}
}
// The base class for the different types of items the List can contain
abstract class ListItem {}
// A ListItem that contains data to display a heading
class HeadingItem implements ListItem {
final String heading;
HeadingItem(this.heading);
}
// A ListItem that contains data to display a message
class MessageItem implements ListItem {
final String sender;
final String body;
MessageItem(this.sender, this.body);
}