Building a form with validation
Apps often require users to enter information into a text field. For example, we might be working on an app that requires our users to log in with an email address and password combination.
In order to make our apps secure and easy to use, we can check whether the information the user has provided is valid. If the user has correctly filled out the form, we can process the information. If the user submits incorrect information, we can display a friendly error message letting them know what went wrong.
In this example, we’ll see how to add validation to a form with a single text field.
Directions
- Create a
Formwith aGlobalKey - Add a
TextFormFieldwith validation logic - Create a button to validate and submit the form
1. Create a Form with a GlobalKey
First, we’ll need a Form
to work with. The Form Widget acts as a container to group and validate
multiple form fields.
When we create the form, we’ll also need to provide a GlobalKey.
This will uniquely identify the Form that we’re working with, and will allow
us to validate the form in a later step.
// Define a Custom Form Widget
class MyForm extends StatefulWidget {
@override
MyFormState createState() {
return new MyFormState();
}
}
// Define a corresponding State class. This class will hold the data related to
// the form.
class MyFormState extends State<MyForm> {
// Create a global key that will uniquely identify the Form widget and allow
// us to validate the form
final GlobalKey<FormState> _formKey = new GlobalKey<FormState>();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// Build a Form widget using the _formKey we created above
return new Form(
key: _formKey,
child: // We'll build this out in the next steps!
);
}
}
2. Add a TextFormField with validation logic
We have our Form in place, but we haven’t provided a way for our users to
enter text! This the job of a TextFormField.
The TextFormField Widget renders a material design text input and knows how to
display validation errors when they occur.
How can we validate the input? By providing a validator function to the
TextFormField. If there is an error with the information the user has
provided, the validator function must return a String containing
an error message. If there are no errors, the function should not return
anything.
In this example, we will create a validator that ensures the TextFormField
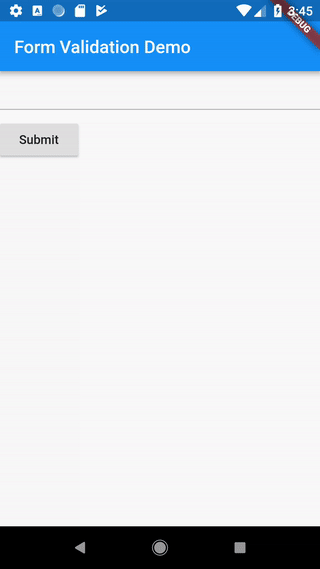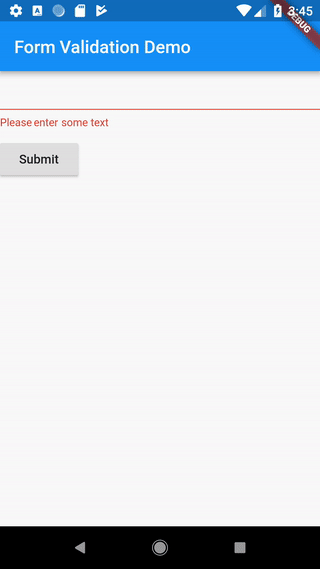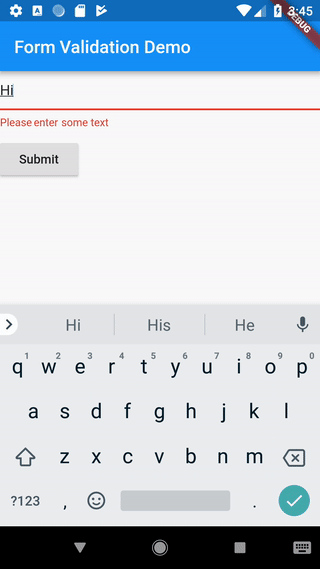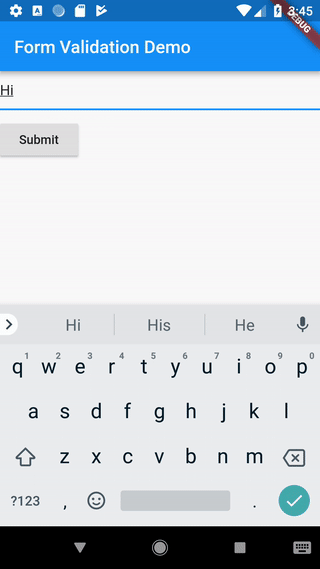
isn’t empty. If it is empty, we will return a friendly error message!
new TextFormField(
// The validator receives the text the user has typed in
validator: (value) {
if (value.isEmpty) {
return 'Please enter some text';
}
},
);
3. Create a button to validate and submit the form
Now that we have a form with a text field, we’ll need to provide a button the user can tap to submit the information.
When the user attempts to submit the form, we’ll need to check if the form is valid. If it is, we will show a success message. If the text field has no content, we’ll want to display the error message.
new RaisedButton(
onPressed: () {
// Validate will return true if the form is valid, or false if
// the form is invalid.
if (_formKey.currentState.validate()) {
// If the form is valid, display a snackbar. In the real world, you'd
// often want to call a server or save the information in a database
Scaffold.of(context).showSnackBar(
new SnackBar(content: new Text('Processing Data')));
}
},
child: new Text('Submit'),
);
How does this work?
In order to validate the form, we’ll need to use the _formKey created in
step 1. We can use the _formKey.currentState method to access the
FormState,
which is automatically created by Flutter when we build a Form.
The FormState class contains the validate method. When the validate method
is called, it will run the validator function for each text field in the form.
If everything looks good, the method returns true. If any text field contains
errors, it will display the error message for each invalid text field and return
false.
Complete Example
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final appTitle = 'Form Validation Demo';
return new MaterialApp(
title: appTitle,
home: new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text(appTitle),
),
body: new MyForm(),
),
);
}
}
// Create a Form Widget
class MyForm extends StatefulWidget {
@override
MyFormState createState() {
return new MyFormState();
}
}
// Create a corresponding State class. This class will hold the data related to
// the form.
class MyFormState extends State<MyForm> {
// Create a global key that will uniquely identify the `Form` widget
final GlobalKey<FormState> _formKey = new GlobalKey<FormState>();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// Build a Form widget using the _formKey we created above
return new Form(
key: _formKey,
child: new Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
new TextFormField(
validator: (value) {
if (value.isEmpty) {
return 'Please enter some text';
}
},
),
new Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 16.0),
child: new RaisedButton(
onPressed: () {
// Validate will return true if the form is valid, or false if
// the form is invalid.
if (_formKey.currentState.validate()) {
// If the form is valid, we want to show a Snackbar
Scaffold.of(context).showSnackBar(
new SnackBar(content: new Text('Processing Data')));
}
},
child: new Text('Submit'),
),
),
],
),
);
}
}